The Evolution and Impact of Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles in the Healthcare Industry
1. Introduction
Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles; In today’s fast-growing world, every realm, whether small or large, is expanding with innovations and ideas. The healthcare industry is also leveraging the latest technologies to provide facilities for patients to better their quality of life. A mode of transportation that facilitates the swift egress of patients is of utmost importance to modern society, where time is of the essence. While the doctor plays a crucial role in a patient’s life, the method of medical transportation has also advanced over time. An ambulance is more than just a landmark in the healthcare industry, as it signifies groundbreaking improvements in medical technologies and standards for transferring patients between facilities. Advances in medical treatments and technical advancements in ambulance vehicles have had some impact on the quality of care rendered during patient transport.
Ambulances, or specially equipped vehicles for transporting patients to hospitals or therapy centers, have progressed from horse-drawn wagons equipped with only the most basic patient transport services to advanced medical equipment such as heart defibrillators, medication, pain relief equipment, monitoring equipment, and others. An ambulance is typically capable of providing patient care en route to the hospital, so their healthcare team or emergency workers are ready for any kind of medical emergency. Additionally, these are long and low metal boxes with a window, allowing the injured or ill inside to be quickly loaded. Over the years, these ambulances have demonstrated that innovation is essential to delivering patient medical services that align with consumer values. Extensive improvements in medical intelligence services have transformed the Mercedes ICU vehicle from simple medical vehicles to fully equipped advanced life service units over time.
1.1. Background and Significance Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles
The primary focus of this report is to inform readers about the development and uptake of fully equipped state-of-the-art vehicles as a vital requirement and a unique need. The section below thus seeks to explore the evolution of regular and emergency patient transfer services and treatment over time. A brief tutorial on the evolution of the vehicles used to provide care paves the way to the topic at hand, presenting a significant historical figure within the field of manufacturers and new technological advancements. Finally, some inkling is given to the emphasis the healthcare system places on logistics and incorporating advancements in technology.
Patient transportation and patient transfers range from a mere 18th-century sedan chair to the present-day requirement of a mobile treatment center. In the depths of winter 1912, a milestone was reached with 20 million kilometers driven and 60,000 journeys since its creation in 1898. A pioneer in the design and manufacture of safe and representative vehicles specifically for ambulance duty, the challenge to modern-day healthcare environments is no different and requires the same inroad in the solution to the existing problem: If healthcare is primarily about delivering patient care, then why would logistics, such as buying and stocking medicines, patient transport, linen management, and general supplies, feature so high on the focus of a health service? From an overview such as this, and a microscopic ‘treatment pitch’ that requires world-class treatment within the vehicle transport to a definite location, it is evident that at least some vehicles are designed with leading-edge technology as a heartbeat. These reasons and discussions help to lead us to ‘Why ICU Vehicles’. In modern-day vehicle design, the notions of logistics have been woven into these ambulances and brought about vehicles such as those designed by their present day. For vehicle standards and design, every country has a set of regulations and minimum standards; hospitals set standards for vehicles that they will work with.
1.2. Purpose and Scope
The analysis completed in this document attempts to explain the evolution of a fully equipped Mercedes ICU ambulance vehicle and its probable impact on patient outcomes. The vehicle and the equipment described above are part of an integrated, system-focused approach. The purpose of this study is to explore the impact that the use of fully equipped Mercedes ICU ambulances may have on a patient present at a scene of life-threatening and life-impairing medical emergencies. This analysis, incorporating patient flow decisions, transport times, and patient physiology, holds inherent limitations for both patient care and the practice of healthcare. In order to discuss fully the vehicle, the associated techniques and equipment, the description need not be limited to technical and technological details or advancements. The argument is also a comparative and qualitative study between the vehicle and the overall functioning of the healthcare system, the principles and interaction of management and technology in a system, and the principles of total system care.
The subject of this investigation covers a detailed comparative analysis and is presented with distinguished results and topics for consideration. It captures the introduction of healthcare Mercedes ICU ambulances in Wales and highlights the problem of quantifying their impact in medical emergencies when a patient or patients do not have an established early and ongoing requirement for critical care. Transformations in scene physiology and improved patient journeys are reported. Each year, similar numbers of accidentally ill injured patients are recorded in Wales in contrast to medical/secondary illness patients. Medical patients are mainly the territory of local urgent care services. Modern ambulance services transport acute and emergency patients who have an expected hospital stay of more than 2 days, i.e., trauma and surgical, medical and coronary admissions to health services. Medical patients with an integrated care complex pathway for the pre-hospital environment should be transported by a reliable healthcare system fitted together with effective decision-making protocol technology capable of ensuring that physiopathophysiological acuity scene-subjective resources are matched with directly proportional pathway response, i.e., an upscale or downscale treatment-to-transport acute care model.
2. Technological Advancements in ICU Vehicles
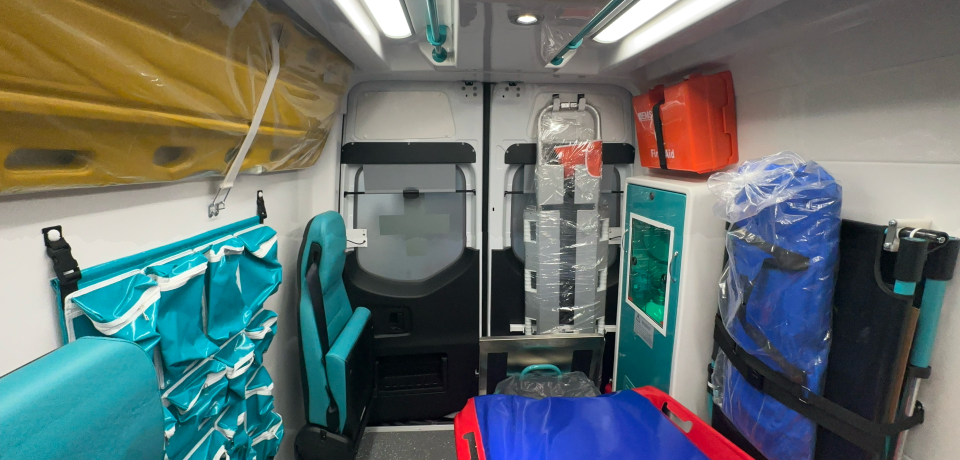
Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles; The concept of fully equipped ICU ambulance vehicles has evolved with technology and vehicle design. In the past, ambulance vehicles only contained a stretcher to move a patient from an accident area to a hospital. In the modern world, secure transportation of a diagnosed patient from one hospital to another or to home care is the challenge for which the emergency medical technician is responsible. The ICU vehicle is the latest of multiple advancements and embodies an achieved level of emergency patient care. In adverse events, life support and primary diagnosis should be immediately available to the patient to improve the chances of survival. ICU vehicles have an overhauled medical cabin in which life support is available for the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of acute patients. It is ready to transport all kinds of emergency patients. Ambulances in earlier times were not technology-enriched vehicles for patient care transport. There are many innovations in design where a modular design and retrofit concept are widely used to accommodate maximum facilities for patients, so necessary care during transport is not curtailed in any sense. They have telemedicine capabilities to consult specialist doctors at any time throughout the journey. They are equipped with innovations like a manual evacuation safe transport stretcher that compensates for a sudden power supply failure during transport. The diagnostic tools include a point-of-care vital monitor, defibrillator, and vital signs diagnostic monitor to look after the patient’s condition during transport. Technological advancements make the vehicle a non-stop care unit. Fully equipped ICU vehicles play a wide role in aiding the healthcare industry to deliver medical facilities for door-to-door transport. User feedback acts as a bridge to establish a roadmap for continuous excellence with enhanced technology developments. Technology is just a part of great design. Engineers working around the facilities should always be in touch with healthcare professionals to help achieve the well-being of the patient. Good design and development based on feedback, business, and people’s value provide assurance, reliability, and trust that the patient is in safe hands, which enhances extended benefits for society. The development of an emergency vehicle also focuses on the overall patient solidarity system.
2.1. Key Features of Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles
The biomedical industry and transportation sector worked together to produce a large number of specially designed health-related transport vehicles in response to anticipated demand. In 2020 alone, more than 1.5 million ambulances were purchased worldwide. Notably, healthcare transportation now involves specialized emergency response vehicles manned by skilled and competent medical teams with the equipment necessary to deliver immediate and critical care to individuals in need. Specialized ambulances have evolved to the point of on-site paramedics and emergency medical physicians. The final generation of ambulances is equipped with a portable ICU and staffed by multidisciplinary medical teams composed of nurses, physicians with subspecialty qualifications, and paramedics and/or physiotherapists.
Fully equipped vehicles are unlike standard ambulances because they are equipped with the best medical devices and equipment. Standard ambulances are equipped with necessary health products in the form of disposable goods. Because their medical devices are used on a large scale, they are less vulnerable since not all patients need them, and doctors thereby use other appropriate disposable medical products. Modern vehicles should be equipped with modular interiors that meet the medical specifications. If a small space is available, only the lightest beds can be provided in order to minimize the weight of the vehicles. The space and lighting must optimize medical activities performed in the vehicle. An adaptable and versatile environment for taking appointments must be maintained. A patient in low-profile cases may necessitate a certain variety of therapeutic beds. The modular interiors of these vehicles are well-designed and simple to clean. All operating units are powered by 12V DC or battery-operated systems. Ergonomic designs make it likely that a global workforce will implement a standard system. This modular environment enables an easy and close viewpoint of the equipment in use and sets the parameters for the availability of AM/ICU and current/old-ups in the rear of the vehicle as needed.
3. Benefits and Challenges of Using Mercedes ICU Vehicles
Mercedes-Benz launched a mobile intensive care unit with the support of the public health system. The car, available in a two- and four-car version, is fully equipped with the latest state-of-the-art medical technology. However, the use of this vehicle also has a number of challenges, including the need for strong financial support from the public health system or other partner networks due to its high acquisition and operating costs. In addition, the operation of the vehicle requires regular adaptation by trained emergency medical staff. Another challenge is the compliance with the conditions for the proper operation of a fully equipped ambulance as an emergency ambulance. The ICU vehicle can be used not only in relation to disasters and major accidents, but can also improve the quality and effectiveness of care that emergency medical services provide in pre-hospital care. The new type of specially equipped rescue vehicle can save crucial moments for patients with severe conditions. As a result, patients increase their chances of a meaningful life, the length of which is not affected.
The use of fully equipped Mercedes ICU vehicles has a number of benefits, especially if appropriately placed in the emergency medical services system. Greater range, flexibility, and coverage are demonstrable advantages of the ICU vehicles. A well-organized network of emergency medical services will ensure minimal patient lag time from emergency rooms or emergency services by reaching advanced care in the form of complete intensive care using the Mercedes-Benz vehicle. Currently, the success of treating a patient or increasing the chances for survival of severely injured people does not depend only on the logistics of the vehicle, the medical equipment, and the trained medical staff. The use of this special car is especially useful in relation to pre-hospital inpatients, as the vehicle’s diagnostic technology ensures that the rescue brings the patient to the institution immediately. By joining the patient already in the field, they can have the most severe condition stabilized on the way to a suitable hospital facility.
3.1. Benefits of Fully Equipped ICU Vehicles – Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles
Fully equipped ICU vehicles, especially those manufactured by Mercedes, provide a wealth of benefits. Firstly, they exert a significant impact on the mobility of offering healthcare services, particularly those facilities that provide access to critical care. Trauma and medical emergencies often require timely access to advanced medical treatments, which transport-time research has shown to be associated with lower time-sensitive mortality rates. Given the unpredictability of the time and location of emergencies, mobile critical care units often accompany other bodies of emergency services such as law enforcement. The vehicle-based ICUs can assess and treat or stabilize patients and gradually streamline the handover to the hospital-based health professionals. Secondly, mobile ICUs provide lifelike critical care just as health facilities do, thereby maintaining their ethical obligation to preserve life. This fidelity to health system care enriches capabilities in population health and protects the health sector’s resources. Specifically, they provide immediate medical intervention in case of clinical or machine-based alarms during patient transportation to the health facilities. Thirdly, mobile ICUs improve patient readmission rates and mortality due to expedited patient stabilization in case of clinical emergencies. To this end, providing timely critical care can mitigate patient health issues and alleviate resource utilization. Integrated care would assign some healthcare services such as the radio communication team, the clinical team, and use comprehensive teamwork to implement patient transitions in time and clinical characteristics between the health facilities and the mobile ICUs. Fourth, mobile ICUs can standardize operational moves and provide smooth, efficient, and effective operation out of the right-of-way logistics. Real-world practitioners similarly believe in the effectiveness of this approach. From an operator’s point of view, the need for reliable high-comfort mobile healthcare units was perceived by emergency medical staff and nurses who desired an effective and feasible environment for the diagnosis and treatment of patients, prognosis, and guideline therapy recommendations. Finally, dedicated companies in the U.S. ensure rapid, regular, and efficient care delivery. They often transport health professionals and return the vehicle to their company.
4. Case Studies and Success Stories – Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles
As we have detailed, the introduction of the concept of Mercedes as a standard for paramedical vehicles has brought many reforms to health care systems. We have collected reports on a number of medical emergencies in which fully equipped ICU vehicles can be an advantage. They claim that the addition of ‘Sprinters’ to their mobile service has significantly increased the perceived quality and speed of healthcare in their catchment areas. We asked them about the challenges of operating the vehicles in real settings. From the above data, we therefore suggest that there are immediate benefits to the current users of fully equipped ICU vehicles. They do indeed provide a viable form of BLS care that, because of their staff, speed, and digital abilities, shortens the period of treatment in and around the ‘golden hour’ and reduces the backlog of patients needing advanced care in the FOB place.
In urban areas, many patients are directly brought to the ED after an MVA or another accident, but the vehicles are used every day in the centers. Hospitals appreciate improving their dispatch situation or reducing queue depth in their ‘receiving center’ (in both urban, rural, municipal, county, and private EDs, inland and coastal). Nurses and doctors appreciate the improved patient service from rigged-up vehicles; they feel they offer better medical care and perceive the vehicles as easier to use, and this affects them in a positive way. The main nurse or registrar in three hospitals gave us written testimonials: We had a 2-3 hour wait from ‘clean vehicles’ arriving after an MVA until we could process them through our busy ED three nights a week. I think the ER runs a lot more smoothly; waiting time is almost nil now. Very efficient system – clean handover and documentation, patients very well prepared for the ER, works well with our DR system. A typical patient is usually a poor ASA degree 4-5 victim; it really helps. I don’t go to the crash scene unless it is a high acuity immediate patient, but I do go to assess the patient in the department before transfer – I guess nurses are the same! Overall advantage after teething problems. We think that it is a win-win for everybody.
4.1. Real-world Applications in Healthcare Settings – Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles
Patient recovery and clinical outcomes go beyond a hospital’s walls. Cases in many countries highlight the need for state-of-the-art medical transportation solutions built into ambulances. Head injury can quickly lead to death if not properly managed by a doctor on the scene and all along the way to a treatment center. Five cases of urban ECMO resuscitation with 24-hour survival were noted. One of the retellings focused on a woman without a pulse for 1 hour and 16 minutes before receiving ECMO at the scene, who was transported on a fully equipped Mercedes ICU vehicle. Another woman in severe heart failure who experienced a 30-minute cardiac arrest lived through a 6.6-hour retrieval insight on ECMO using an ambulance. The detailed cases emphasize the importance of innovative medical equipment and preparation, from hospital resources to ambulance services. In Switzerland, the incorporation of a specialized ECPR vehicle into Zurich rescue services was a parallel success. Researchers and focus groups with EMS personnel, RNs, nurse practitioners, and pediatric intensivists collected ideas from staff about how a mobile ICU should function. Nearly a consensus view, the staff saw a mobile ICU as the default vehicle for all interfacility transports. Empowered, the virtual ‘blank slate’ vehicle was viewed as the go-to for regional deployments during times of day or times of year when ‘all units were busy.’ The local staff collectively agreed on the adaptability of the vehicle among different healthcare practitioners, the first ECN, an air medical outreach coordinator, and an area EMS director. One ED physician described the vehicle as ‘portable healthcare delivery.’ These individual descriptions of the vehicle agree with the consensus vision: it’s an ICU in a van. An ED physician had a more singular view of the vehicle’s best use: that it ‘really helps emergency preparedness at the local hospital level.’ This focus is not patient-centered, but access and practice-centered, a subtle difference in mindset.
5. Future Trends and Innovations – Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles
It is always a hazardous venture to predict the future, but since we know that Mercedes has been at the forefront of developing and constructing mobile ICU vehicles for a very long time, with some of the first vehicles constructed by this manufacturer still going strong, it is not completely off the mark to speculate in which direction their design and function might develop. Medicine and healthcare are constantly evolving, and we can anticipate some of the changes that might influence the development and production of such vehicles. More automation and more digitalization, extending already existing trends towards AI-driven diagnostics, telemedicine, and the digitalization of patient records and management, are likely to result in vehicles that take the greater demands placed on their function and design into consideration. We can expect vehicles ready and equipped to deal with this kind of high-tech medical care in a future generation of mobile ICUs. We can also anticipate a development towards more attention to environmental concerns and an ongoing drive to build electric vehicles – where luxury, comfort, and ease of driving may become as important as technology and equipment. The development of hybrid vehicles might also be a possible future direction in a bid to overcome some of the challenges of diesel engines. The progress of vehicle regulation and certification will also likely favor such vehicles, especially if more emphasis starts to be placed on the reduction of pollutants and carbon dioxide emissions from ambulances. The movement in the organization of healthcare and individual patient contacts with health services is especially likely to offer a strong driving force for the coming mobile ICUs. National guidelines exist regarding where to take patients with certain diseases or problems, and protocols are followed according to the extent and severity of the individual patient’s disease. Up to date, the routine and national guidelines have been collected in different folders and papers connected to the ambulance, including the ambulance services’ national instruction manuals, which have been used to confirm the correct examination and treatment. The new way of working will offer greater possibilities in the mobilization and care for the patient – very ill and injured patients will be able to be treated by mobile ICUs at the scene of illness, or road traffic accidents, and in a patient’s own home in order to avoid a hospital visit, which will be at odds with the existing policy for the healthcare community. The new mobile ICU vehicles will have adapted their vehicles and will be able to bring more advanced equipment than previously. They will be ready to perform certain invasive procedures that have traditionally taken place in intensive care departments, like ventilator and intravenous drip, as well. They will also be able to offer the patient more intensive pain relief with the administration of the drugs available in the hospital. It will, however, take some time before the vehicles are actually released for work as mobile ICUs. Any changes to the existing vehicles will need to be thoroughly validated, which means they have to be tested in great depth. In the same way, the public health system will still control the medical rules the military needs to meet, and they will not be able to use their vehicles adapted as a mobile ICU.
5.1. Emerging Technologies in ICU Vehicles – Fully Equipped Mercedes ICU Vehicles
In this subsection, we look into the possibilities of emerging technologies in ICU vehicles. The primary aim is to continue our trend in medical transportation. With rapid advancements in the field of emerging technologies, societies are moving toward smart and intelligent transportation systems, and the health industry is no exception. Fully equipped modern ICU cars are seen as flying ambulances by many people. However, little to no effort has been made to show that a flying ambulance is needed. Having flying ambulances would certainly impact urban societies. Nowadays, with the integration of telehealth facilities and real-time patient monitoring systems, better quality patient support and medication are possible. Furthermore, introducing data analytics in route planning, combined with the patient’s clinical conditions and the concentration of COVID-19 cases in certain areas, will shed more light on the availability of required resources and the time needed to transport the patient to their destination, hence optimizing resources and the fight against COVID-19. New notions are also more appealing than designing flying ambulances at this moment, especially to all the different authorities.
Electric vehicles are also considered in future designs not only because they are environmentally friendly to support this direction, but also because the green technologies used in vehicle manufacturing have a certain influence when considering the increase of COVID-19 cases and the different pandemic waves. The design should reflect the need to integrate potential COVID-19 and other pandemics—adjusting quickly to redesigns when a new pandemic occurs—inside the ICU vehicles, especially in the filter and air conditioning units. New findings should ideally be used in further attempts when the risks of the pandemic are minimized. Today, remote care in emergency medical services is one of the perspectives of telemedicine research. Real-time diagnostic quality and decision support can be delivered in immersive augmented reality environments, which can be created in 3D simulations by pre-formatted situations managed only by the urgency situation leader. These innovative technologies shift from a skilled human-intervention strategy to a virtual professional team. A decision-making environment can manage groups of patients even on extended medical directions for patients’ vital parameters and drug delivery. Data-consuming computing solutions can be linked to the 3D simulation for records and immersive landscape file details. A new approach, named friendly urgent decision systems, can influence many conscious situations and show the seamless blend of healthcare and technological development.